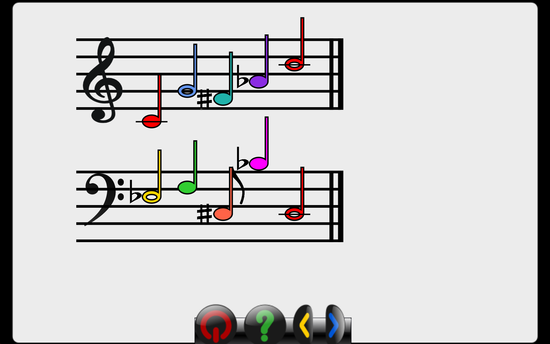
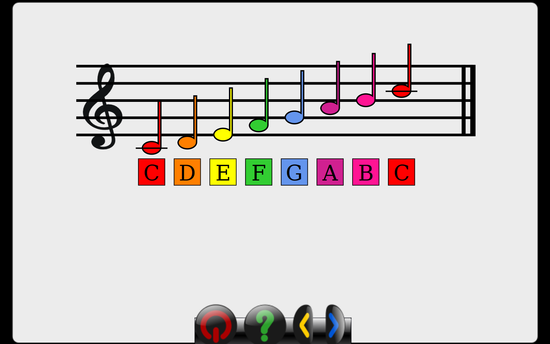
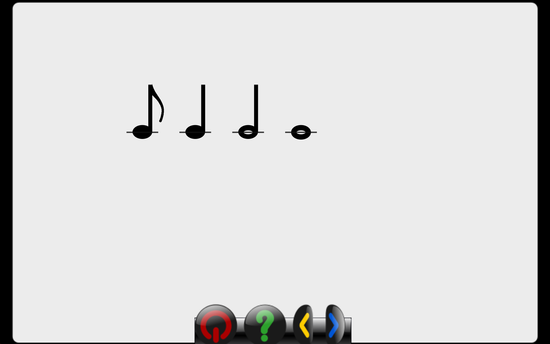
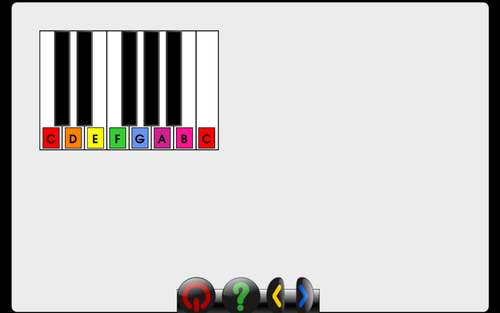
Adding a music activity and using gcomprismusic.py module
If you wish to add an activity relating to music to gcompris, consider importing the module gcomprismusic.py This module contains several useful classes of objects that will not only make it easier for you to make your activity, but also help GCompris maintain a more uniform music platform.
The following music objects are currently included in the module:
- Musical Staff
- Bass Clef
- Treble Clef
- Music Note
- Eighth Note
- Quarter Note
- Half Note
- Whole Note
- Piano Keyboard
- General Utility Functions
The module was developed in 2012 by Beth Hadley through Google Summer of Code. It can always be improved, added to, and adjusted.
The documentation provided below will help you get started using the module. It provides coding examples, with pictures, that will help you create music objects. Not all, but most, methods and properties are documented.
Beth Hadley welcomes comments, ideas, contributions, and questions regarding the gcomprismusic module or GCompris music activities. Bug reports are welcome as well, file on GCompris' bug tracker or send me an email. (bethmhadley@gmail.com)
Contents
- 1 How to import the gcomprismusic module
- 2 General Reference
- 3 Staff Classes
- 3.1 Staff Formatting Attributes
- 3.2 Music Notation Formatting
- 3.3 Note & Playback
- 3.4 Methods
- 3.4.1 drawStaff()
- 3.4.2 drawNote(self,note)
- 3.4.3 writeLabel(self, text, note)
- 3.4.4 eraseOneNote(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None)
- 3.4.5 eraseAllNotes(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None)
- 3.4.6 clear(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None)
- 3.4.7 playComposition(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None, playingLineOnly=False)
- 3.4.8 stringToNotation(self, melodyString)
- 3.4.9 file_to_staff(self, filename)
- 3.4.10 staff_to_file(self)
- 3.4.11 drawScale(self, scaleName, includeNoteNames=True)
- 3.4.12 colorCodeAllNotes(self)
- 3.4.13 colorCodeAllNotes(self)
- 3.4.14 colorAllNotes(self, color)
- 3.4.15 getNoteXCoordinate(self)
- 3.4.16 getNoteYCoordinate(self)
- 4 Note Classes
- 5 PianoKeyboard Class
- 6 General Utility Functions
- 6.1 textButton(x, y, text, self, color='gray', width=100000)
- 6.2 textBox(text, x, y , self, width=10000, fill_color=None, stroke_color=None, noRect=False, text_color="black")
- 6.3 ready(self, timeouttime=200)
- 6.4 displayIncorrectAnswer(self, nextMethod)
- 6.5 displayYouWin(self, nextMethod)
- 6.6 displayIncorrectAnswer(self, nextMethod)
- 6.7 pianokeyBindings(keyval, self)
How to import the gcomprismusic module
The gcomprismusic.py module is located in the piano_composition-activity. There are certain resources that support the module, and these are permanently located under the resources folder of the piano_composition activity. Thus, you must execute the following instructions to properly import the gcomprismusic module.
- create your new activity (see Beginner if you need help)
- open init_path.sh and find the
pythonplugindirline. Replace this line with something like:pythonplugindir=$path/../piano_composition-activity:$path/../name_of_your_activity-activity
save and close this file - add a resources folder to your activity folder
- create a symbolic link in this resources folder that references the piano_composition resources file. If you are unsure of this step, just go into the play_piano activity folder, click on resources, and copy the
piano_compositionfolder and paste that into your resources folder - open the python file for your activity,
name_of_your_activity, and find at the top where all the import statements are. add the following line to the import statements:from gcomprismusic import *
- run your activity, and ensure that it works (you should see a screen that says "This is the first plugin in GCompris coded in the Python Programming language." If there are errors, enjoy troubleshooting or contact Beth.
General Reference
Once you've imported the module, you may call or invoke all methods and classes. Instructions and examples are provided below for your reference.
- Each note is assigned a number, stored internally as
numIDThis is to prevent issues with converting between different language translations of note names. Each note is also assigned a color, according toNOTE_COLOR_SCHEMEUnfortunately. currently only two octaves of notes are supported (bass clef C in the staff to treble clef C in the staff). Future improvements may include expanding the pitch possibilities to include both higher and lower notes. This is not difficult (I could do it if an activity needed it, and may prove to be a good task for an eager beginner). The following table represents the currently available notes:English Name Northern European Name numID Color C C 1 C sharp / D flat (C♯ / D♭) Cis / Des -1 D D 2 D sharp / E flat (D♯ / E♭) Dis / Es -2 E E 3 F F 4 F sharp / G flat (F♯ / G♭) Fis / Ges -3 G G 5 G sharp / A flat (G♯ / G♭) Gis / As -4 A A 6 A sharp / B flat (A♯ / B♭) Ais / B -5 B H 7 C (higher octave) C (higher octave) 8
- getKeyNameFromID(numID, sharpNotation=True)
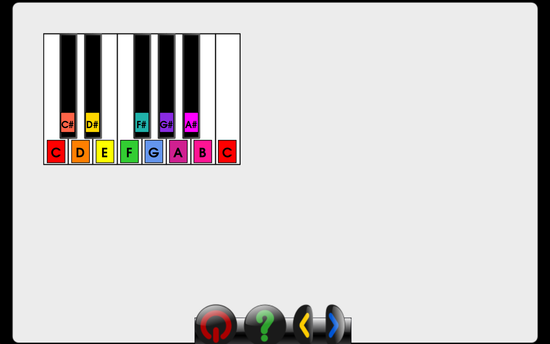
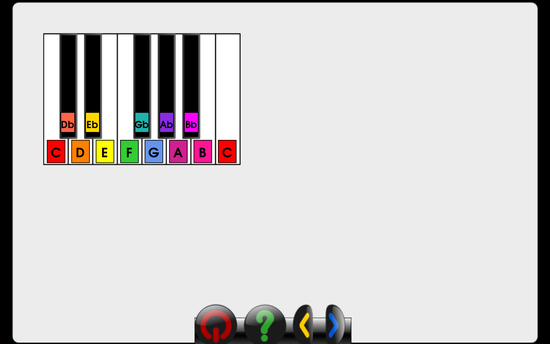
get the name of the key that corresponds to the numID given. optionally set sharpNotation = True for sharp notation, or sharpNotation = False for flat notation >>> getKeyNameFromID(1) C >>> getKeyNameFromID(-3, sharpNotation=True) F# >>> getKeyNameFromID(-5, sharpNotation=False) Bb
- getIDFromKeyName(keyName)
get the name of the key that corresponds to the numID given >>> getIDFromKeyName('C') 1 >>> getIDFromKeyName('D#') -2 >>> getIDFromKeyName('Eb') -2
Staff Classes
There are two staff subclasses, both of which inherit from the master Staff Class:
- TrebleStaff
- BassStaff
To create these objects, the __init__ functions require the following arguments:
x: starting x position of the staffy: starting y position of the staffcanvasRoot: the rootitem of the canvasnumStaves: the number of staves you'd like to create
An example of instantiating each object is below. Note that you must call the drawStaff() method to draw the staff to the canvas.
>>> self.staff1 = TrebleStaff(50, 30, self.rootitem, numStaves=1) >>> self.staff2 = BassStaff(50, 130, self.rootitem, numStaves=2)
Staff Formatting Attributes
| Attribute Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
endx
|
390 | width of staff lines |
verticalDistanceBetweenStaves
|
115 | vertical distance between musical staves |
staffLineSpacing
|
13 | vertical distance between lines in staff |
staffLineThickness
|
2.0 | thickness of staff lines |
numStaves
|
from __init__ | number of staves to draw |
Music Notation Formatting
| Attribute Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
initialNoteX
|
30 | starting X position of first note |
noteSpacingX
|
26 | distance between each note when appended to staff |
dynamicNoteSpacing
|
False | adjust note spacing according to space needed by each note |
currentLineNum
|
1 | the line number you're currently writing notes to |
currentNoteType
|
4 | the note type you're currently using to write to the musical staff, could be 4 (quarter), 8 (eighth), 2 (half) or 1 (whole) |
Note & Playback
| Attribute Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
initialNoteX
|
30 | starting X position of first note |
colorCodeNotes
|
True | color notes according to NOTE_COLOR_SCHEME
|
labelBeatNumbers
|
False | label the beat numbers for each note above the note (used in play_rhythm-activity)
|
drawPlayingLine
|
False | draw vertical line on staff to follow the beat as the composition is being played |
notReadyToPlay
|
False | #set to True when staff is not ready to play composition (something else is going on for example) |
noteList
|
[]
|
list of note objects written to staff |
staffName
|
'trebleClef' or 'bassClef' | name of the staff |
positionDict
|
{set values} | a dictionary mapping the notes to the appropriate y coordinate on the staff |
Methods
drawStaff()
- draw the staff, including staff lines and staff clefs
self.newStaff = TrebleStaff(100, 80, self.rootitem, numStaves=4)
self.newStaff.drawStaff(self)
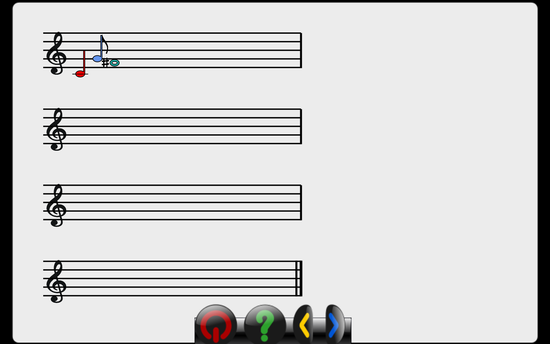
drawNote(self,note)
- determine the correct x & y coordinate for the next note, and writes this note as an image to the staff. An alert is triggered if no more room is left on the staff. Color-codes the note or draws beat numbers if appropriate.
self.newStaff = TrebleStaff(50, 50, self.rootitem, numStaves=4)
self.newStaff.drawStaff()
self.newStaff.drawNote(QuarterNote(1, 'trebleClef', self.newStaff.rootitem))
self.newStaff.drawNote(EighthNote(5, 'trebleClef', self.newStaff.rootitem))
self.newStaff.drawNote(WholeNote(-3, 'trebleClef', self.newStaff.rootitem))
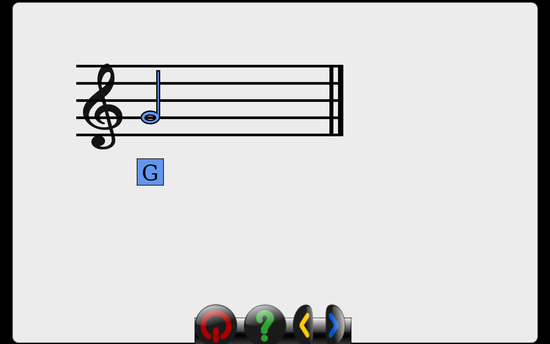
writeLabel(self, text, note)
- writes the text below the note, such as labeling the note name, in color-code if self.colorCodeNotes = True
self.newStaff = TrebleStaff(50, 50, self.rootitem, numStaves=1)
self.newStaff.endx = 200
self.newStaff.rootitem.scale(2.0, 2.0)
self.newStaff.drawStaff()
n2 = HalfNote(5, 'trebleClef', self.newStaff.rootitem)
self.newStaff.drawNote(n2)
self.newStaff.writeLabel('G', n2)
eraseOneNote(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None)
- removes the last note in the staff's noteList, updates self.currentLineNum if necessary, and updates self.currentNoteXCoordinate
self.newStaff.eraseOneNote()
eraseAllNotes(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None)
- remove all notes from staff, deleting them from self.noteList, and restores self.currentLineNumto 1 and self.currentNoteXCoordinate to the starting position
self.newStaff.eraseAllNotes()
clear(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None)
- clear all notes and clefs on the staff (for preparation of a clef change)
self.newStaff.clear()
playComposition(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None, playingLineOnly=False)
- plays entire composition. establish timers, one per note, called after different durations according to noteType. Only way to stop playback after calling this method and during play is self.eraseAllNotes()
self.newStaff.playComposition()
stringToNotation(self, melodyString)
- parse the melody string and write the notes to the staff. The melody must be in a very simple format. It is one line, and begins the clef, either 'trebleClef' or 'bassClef' Then, each following note is seperated with a space and the note name (English system, sharp=#,flat=b, C (second octave is 2C rather than just C) written first followed by the note duration (8=eighth,4=quarter,2=half,1=whole)
self.staff1 = TrebleStaff(50, 30, self.rootitem, numStaves=1)
self.staff1.endx = 200
self.staff1.rootitem.scale(2.0, 2.0)
self.staff1.drawStaff()
self.staff1.stringToNotation('trebleClef C4 G2 F#4 Ab4 2C2')
self.staff2 = BassStaff(50, 130, self.rootitem, numStaves=1)
self.staff2.endx = 200
self.staff2.rootitem.scale(2.0, 2.0)
self.staff2.drawStaff()
self.staff2.stringToNotation('bassClef Eb2 F4 C#8 Bb4 C2')
file_to_staff(self, filename)
- open text file, read contents and write to staff
self.newStaff.file_to_staff('/dir/to/name_of_text_file.txt')
staff_to_file(self)
- convert staff to notation, write to text file, save to MyGCompris folder
self.newStaff.staff_to_file()
drawScale(self, scaleName, includeNoteNames=True)
- return a note's vertical coordinate based on the note's name. This is unique to each type of clef (different for bass and treble). ScaleNames currently supported: 'C Major'
self.staff2 = TrebleStaff(50, 50, self.rootitem, numStaves=1)
self.staff2.endx = 300
self.staff2.rootitem.scale(2.0, 2.0)
self.staff2.drawStaff()
self.staff2.drawScale('C Major')
colorCodeAllNotes(self)
- color notes according to
NOTE_COLOR_SCHEME
self.newStaff.colorCodeAllNotes()
colorCodeAllNotes(self)
- color notes according to
NOTE_COLOR_SCHEME
self.newStaff.colorCodeAllNotes()
colorAllNotes(self, color)
- color all notes a certain color ('black', 'red', 'blue', etc.)
self.newStaff.colorAllNotes('black')
getNoteXCoordinate(self)
- determines the x coordinate of the next note to be written to the staff, with consideration for the maximum staff line length. Increments
self.currentLineNumand setsself.currentNoteXCoordinate
getNoteYCoordinate(self)
- return a note's vertical coordinate based on the note's name. This is unique to each type of clef (different for bass and treble)
Note Classes
There are four types of notes classes, all of which subclass the Note class.
- Eighth Note
- Quarter Note
- Half Note
- Whole Note
To create these objects, the __init__ functions require the following arguments:
numID: The numerical id number that corresponds to this note (see table above for note number correspondance)staffType: 'trebleClef' or 'bassClef', whichever clef this note will belong torootitem: the rootitem of the canvas where you'd like this note to appear (use the staff's rootitem if you'd like the note to appear in the staff)sharpNotation=Trueoptional argument, pass in False if you'd like this note to always display with flat notation. Default is to display with flat notation
An example of creating notes (these will not appear on the page until you call the draw() method)
>>> n8 = EighthNote(1, 'trebleClef', self.rootitem) >>> n4 = QuarterNote(1, 'trebleClef', self.rootitem) >>> n2 = HalfNote(1, 'trebleClef', self.rootitem) >>> n1 = WholeNote(1, 'trebleClef', self.rootitem)
Each note has an x and y coordinate, set to 0,0 initially but updated when it is drawn to the canvas.
| Property Name | Value(s)/Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | 0 | x-position of note when written to canvas (updated when .draw() is called |
| y | 0 | y-position of note when written to canvas (updated when .draw() is called |
| staffType | from __init__ | the staffType ('trebleClef' or 'bassClef' this note corresponds to |
| sharpNotation | from __init__ | toggle to switch note between sharp notation and flat notation, if applicable |
| noteType | Eighth:8, Quarter:4,Half:2, Whole:1
|
the number that corresponds to the note name |
| beatNums | Eighth:['+'],Quarter:['1'],Half:['1','2'],Whole:['1','2','3','4']
|
the beat numbers that correspond to the notes |
| millisecs | Eighth:250, Quarter:500,Half:1000, Whole:2000
|
millisecond length of each note (for use during composition playback |
Methods
draw(self, x,y)
- places note image in canvas at x,y
n2 = QuarterNote(5, 'trebleClef', self.rootitem)
n2.rootitem.scale(2.0, 2.0)
n2.draw(100, 100)
play(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None)
- plays the note pitch. Each pitch is stored in the resources folder as an .ogg file (these are not synthesized)
self.newStaff = TrebleStaff(100, 80, self.rootitem, numStaves=4)
self.newStaff.drawStaff(self)
color(self, color)
- color the note a certain color ("black", "blue", or html tags)
colorCodeNote(self)
- color the note the appropriate color based on the given color scheme
enablePlayOnClick(self)
- enables the function that the note will be played when the user clicks on the note
disablePlayOnClick(self)
- disables the function that the note will be played when the user clicks on the note (same as self.silent=True)
highlight(self)
- highlight the note for self.millisecs, then revert (used during playback)
remove(self)
- remove the note (delete the note's rootitem)
PianoKeyboard Class
This is an object representing one-octave of a piano keyboard
To create a PianoKeyboard, the __init__ function takes:
x: The x coordinate of the keyboardy: The y coordinate of the keyboardcanvasroot: The rootitem of the canvas
The PianoKeyboard class has the following attributes:
| Attribute Name | Value/Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| blackKeys | False | include black keys as buttons |
| whiteKeys | True | include white keys as buttons |
| sharpNotation | True | use sharp notation when labeling keys and writing notes to staff |
| colors | dictionary set to NOTE_COLOR_SCHEME
|
the colors to use for each key, default set the same as the note's color scheme |
Methods
draw(self, width, height, key_callback)
- draw the staff, including staff lines and staff clefs
def keyboard_button_press(self, widget=None, target=None, event=None):
pass
p = PianoKeyboard(50, 50, self.rootitem)
p.draw(300, 200, keyboard_button_press)
- or before drawing, use:
p.blackKeys=True
- or before drawing, use:
p.sharpNotation=False
General Utility Functions
These are just a few methods I wrote that I used quite often throughout my activities, that might be useful to you.
textButton(x, y, text, self, color='gray', width=100000)
- Add a text button to the screen with the following parameters
x: the x position of the buttony: the y position of the buttontext: the text of the buttonself: the self object this button is to be written to (just pass 'self')color: the color of button you'd like to use. Unfortunately there
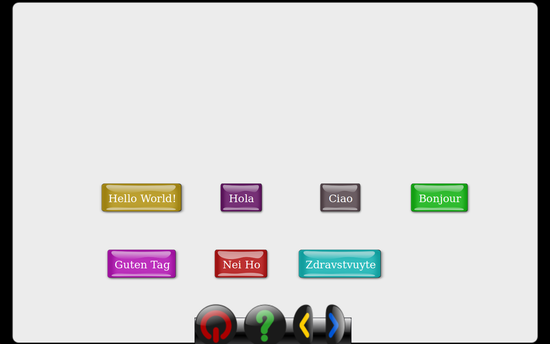
textButton(200, 300, 'Hello World!', self, color='brown')
textButton(350, 300, 'Hola', self, color='darkpurple')
textButton(500, 300, 'Ciao', self, color='gray')
textButton(650, 300, 'Bonjour', self, color='green')
textButton(200, 400, 'Guten Tag', self, color='purple')
textButton(350, 400, 'Nei Ho', self, color='red')
textButton(500, 400, 'Zdravstvuyte', self, color='teal', width=70)
textBox(text, x, y , self, width=10000, fill_color=None, stroke_color=None, noRect=False, text_color="black")
- write a textbox with text to the screen. By default the text is surrounded with a rectangle. Customize with the following parameters:
text: the text to writex: the x position of the texty: the y position of the textself: the self object this text is to be written to (just pass 'self')width: the width limit of the textfill_color: the color to fill the rectanglestroke_color: the color to make the rectangle linesnoRect: set to true for no rectangle to be drawntext_color: the color of the text, accepted colors include string html color tags or english names
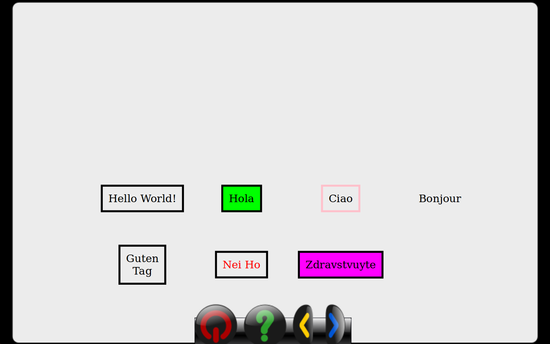
textBox('Hello World!', 200, 300, self)
textBox('Hola', 350, 300, self, fill_color='green')
textBox('Ciao', 500, 300, self, stroke_color='pink')
textBox('Bonjour', 650, 300, self, noRect=True)
textBox('Nei Ho', 350, 400, self, text_color='red')
textBox('Guten Tag', 200, 400, self, width=10)
textBox('Zdravstvuyte', 500, 400, self, fill_color='#FF00FF')
ready(self, timeouttime=200)
- function to help prevent "double-clicks". If your function call is suffering from accidental system double-clicks, import this module and write these lines at the top of your method:
if not ready(self):
return False
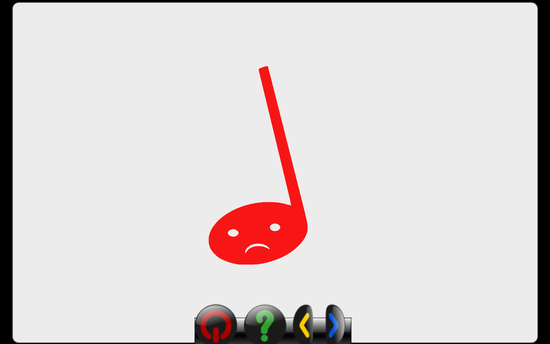
displayIncorrectAnswer(self, nextMethod)
- displays the sad note for 900 milliseconds, then calls
nextMethod(very similar to GCompris' bonus, but uses a sad note instead and has a few more tweaks
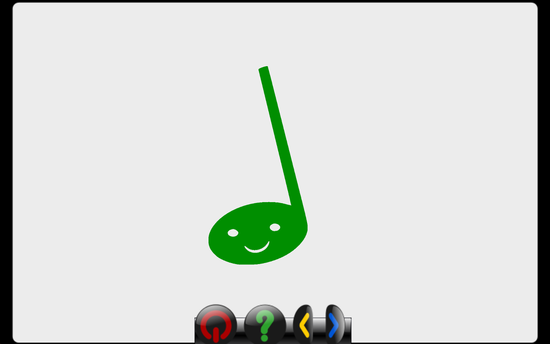
displayYouWin(self, nextMethod)
- displays the happy note for 900 milliseconds, then calls nextMethod (very similar to GCompris' bonus, but uses a happy note instead and has a few more tweaks
displayIncorrectAnswer(self, nextMethod)
- displays the sad note for 900 milliseconds, then calls nextMethod (very similar to GCompris' bonus, but uses a sad note instead and has a few more tweaks
pianokeyBindings(keyval, self)
- nice key bindings for the piano keys (see table mapping keys to functions below). In your activity's key_press method, call this method and pass in the keyval and self:
def key_press(self, keyval, commit_str, preedit_str):
utf8char = gtk.gdk.keyval_to_unicode(keyval)
pianokeyBindings(keyval, self)
| Computer Keyboard Key | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piano Key | C | D | E | F | G | A | B | C (higher octave) | C♯ / D♭ | D♯ / E♭ | F♯ / G♭ | G♯ / A♭ | A♯ / B♭ |